|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready... |
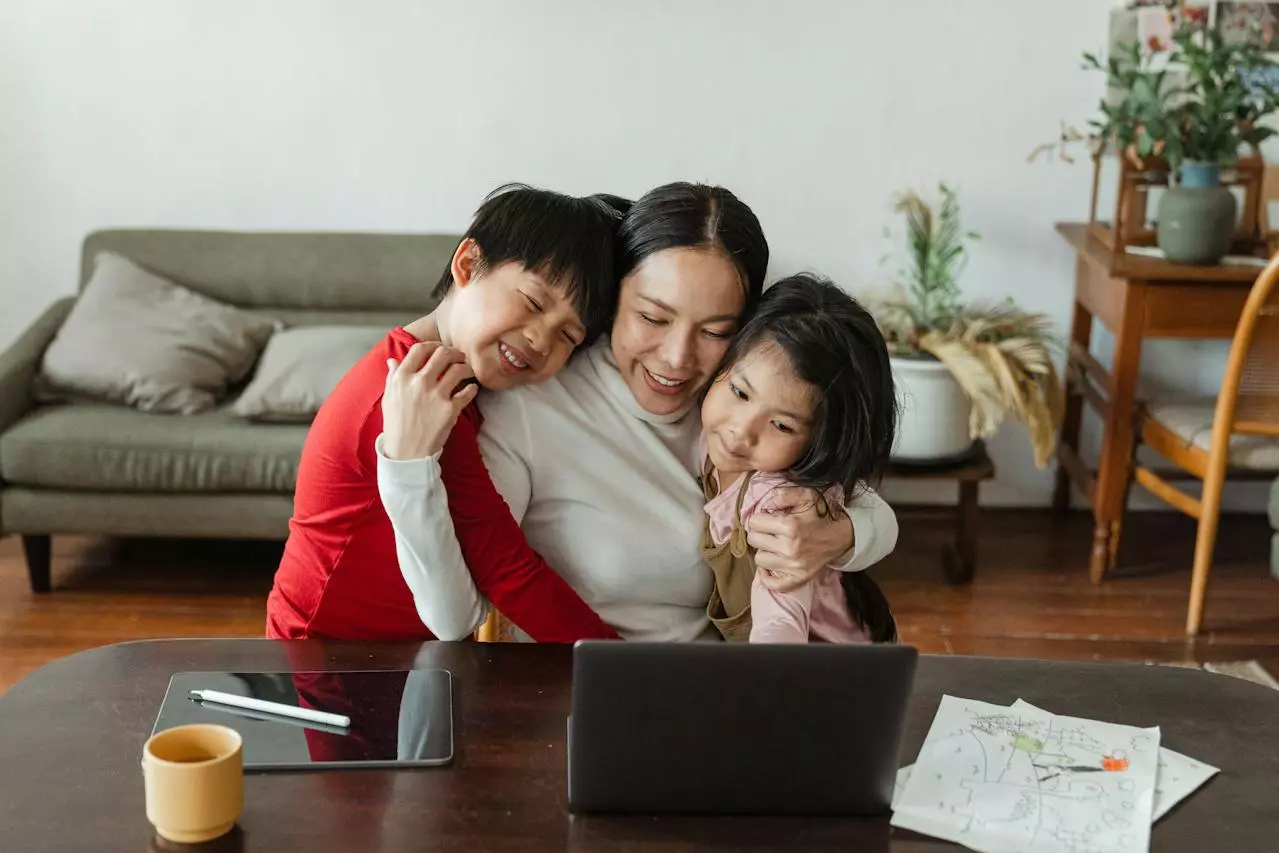
What are modern parenting styles psychology?
Modern parenting styles in psychology reflect contemporary approaches to raising children in the ever-changing social and cultural landscape. In today’s world, modern parenting emphasizes a balance between nurturing and disciplining, aiming to foster a child’s emotional, social, and cognitive development. One prevalent style is modern parenting, characterized by its adaptive nature and focus on open communication and mutual respect between parents and children. This approach encourages parents to be empathetic and understanding, acknowledging their child’s individuality while setting appropriate boundaries.
Another prominent style within the realm of modern parenting is authoritative parenting, which combines warmth and responsiveness with clear rules and expectations. This approach promotes a child’s independence while providing a secure and structured environment. Additionally, there is the concept of permissive parenting, where parents are highly responsive but have few demands, allowing children considerable freedom. On the other hand, authoritarian parenting is characterized by high demands and low responsiveness, often resulting in strict rules without much room for flexibility.
In recent years, the modern parenting landscape has also seen the rise of positive parenting, focusing on positive reinforcement and gentle discipline techniques to foster a child’s self-esteem and emotional well-being. Moreover, attachment parenting has gained traction, emphasizing the importance of forming strong emotional bonds between parents and children through practices like babywearing and co-sleeping.
From my expertise, I can affirm that modern parenting styles are heavily influenced by research in child psychology and behavioral sciences. Professionals emphasize the significance of a nurturing environment that supports a child’s autonomy, self-expression, and emotional intelligence. Informative resources and evidence-based parenting programs are widely available, offering guidance to parents navigating the complexities of raising children in the digital age.
In conclusion, understanding modern parenting styles in psychology involves recognizing the diverse approaches parents take in nurturing their children. With a focus on adaptability, empathy, and clear communication, modern parenting styles aim to create a nurturing environment that supports a child’s overall development. As a parent, staying informed about these various approaches can empower individuals to make well-informed decisions, ensuring the well-being and positive growth of their children.
What is joyful parenting in modern times?
Modern parenting has witnessed a paradigm shift with the emergence of a concept known as “joyful parenting.” In the contemporary context, modern parenting isn’t just about providing for a child’s physical needs; it’s also about nurturing their emotional well-being. Modern parenting emphasizes joy, not just for the child but also for the parents. Joyful parenting in modern times revolves around creating a harmonious balance between structure and spontaneity, discipline and freedom, and guidance and independence.
From my expertise, I can share that joyful parenting in modern times involves being present in the moment, actively engaging with your child, and fostering a positive and loving environment. It’s about finding joy in the small things, celebrating achievements, and embracing failures as opportunities for growth. In the context of modern parenting, joyful parenting encourages parents to be mindful, patient, and understanding, creating a home environment where children feel safe to express themselves and explore the world around them.
Joyful parenting also incorporates the concept of positive reinforcement, focusing on praising effort rather than just achievements. It involves active listening, empathetic understanding, and validating a child’s emotions. By incorporating playfulness, creativity, and humor into everyday activities, parents can create a joyful atmosphere that encourages learning and bonding.
In today’s fast-paced world, joyful parenting in modern times also includes managing parental stress effectively. Parents are encouraged to practice self-care, seek support when needed, and maintain a healthy work-life balance. This holistic approach to modern parenting not only benefits the child’s emotional and social development but also enhances the overall well-being of the entire family.
In conclusion, joyful parenting in modern times within the realm of modern parenting is about fostering happiness and emotional connection within the family. By embracing a positive and mindful approach, parents can create a nurturing environment where children thrive emotionally, intellectually, and socially. It’s about savoring the precious moments of parenthood, creating lasting memories, and building strong, loving relationships that endure the test of time.
What is ABC parenting?
ABC parenting, an acronym for “Authoritative, Balanced, and Compassionate” parenting, represents a holistic approach to raising children. In this method, parents assert their authority while maintaining open lines of communication and understanding. The Authoritative aspect involves setting clear boundaries, providing structure, and enforcing rules, ensuring children understand expectations, thereby fostering a sense of security [1].
The Balanced component signifies the equilibrium between discipline and freedom. It allows children to explore within defined limits, encouraging independence and learning from experiences while ensuring a safety net [2].
Lastly, the Compassionate element emphasizes empathy and emotional support. ABC parents validate their child’s feelings, nurturing a strong emotional bond. This approach enhances a child’s emotional intelligence and self-esteem, crucial for their overall development [3].
ABC parenting doesn’t only focus on academic achievements but also prioritizes emotional well-being. By embracing this approach, parents create an environment where their children feel secure, loved, and respected. This method empowers children to grow into confident, empathetic, and well-rounded individuals, equipped to face life’s challenges with resilience and compassion.
🌐 Sources
- Parenting for Brain – Authoritative Parenting
- NCBI – Authoritative Parenting: Synthesizing Nurturance and Discipline for Optimal Child Development
- NCBI – Parenting Styles and Child’s Emotional Intelligence: What Do We Know?
What are the 3 F’s of effective parenting?
Effective parenting embodies the 3 F’s: Firmness, Fairness, and Flexibility.
Firmness refers to setting clear and consistent boundaries. It involves being assertive while maintaining a nurturing environment. Children thrive when they understand the rules and consequences, establishing a sense of security.
Fairness emphasizes treating each child equitably. Acknowledging their individuality and avoiding favoritism fosters trust and promotes healthy sibling relationships. Fairness also involves considering a child’s perspective, ensuring decisions are just and reasonable.
Flexibility recognizes that parenting strategies need adaptation. Being open to change enables parents to respond to unique challenges and evolving situations. Flexible parents adjust their approach based on a child’s age, temperament, and needs, fostering a supportive atmosphere.
Drawing from my expertise, effective parenting combines these principles, creating a balanced environment. It involves active listening, empathy, and encouragement, nurturing a child’s emotional intelligence. Tailoring disciplinary methods to a child’s temperament and age enhances their understanding and cooperation.
Additionally, parents practicing effective parenting provide positive reinforcement, boosting a child’s self-esteem. By fostering open communication, they create a safe space for their children to express themselves, promoting healthy emotional development.
What are the four parenting rules?
Parenting rules form the backbone of effective child-rearing, providing a structured framework for nurturing healthy, well-adjusted children. The first rule involves consistency. Consistent rules and expectations create stability, offering children a sense of security. When parents maintain consistency in discipline and routines, it fosters a predictable environment where children know what to expect.
The second rule revolves around communication. Open and honest communication builds trust between parents and children. Listening actively and empathetically to a child’s concerns encourages them to express their feelings. Effective communication ensures that parents understand their child’s needs, fears, and aspirations, enabling better support and guidance.
Positive reinforcement forms the third rule. Encouragement and praise for good behavior enhance a child’s self-esteem and confidence. Celebrating achievements, no matter how small, reinforces positive behavior, motivating children to continue making positive choices. Positive reinforcement fosters a nurturing atmosphere, encouraging children to explore and learn while feeling supported.
Lastly, the fourth rule is adaptability. Parenting is not one-size-fits-all; it requires adaptability to cater to each child’s unique personality and needs. Parents need to adjust their approach based on the child’s age, temperament, and developmental stage. Being adaptable allows parents to address challenges effectively and provide appropriate guidance tailored to the child’s specific circumstances.
Drawing from my expertise, these parenting rules are foundational. They help create a loving, stable environment where children can flourish emotionally, socially, and academically. By adhering to these principles, parents foster a strong parent-child relationship, ensuring the child’s holistic development.
What are the Big Five parenting style?
Parenting styles, often categorized into the Big Five, significantly influence a child’s development. The first style, authoritarian parenting, is characterized by strict rules and high demands. Authoritarian parents expect obedience without room for negotiation, potentially hindering a child’s independence but instilling discipline.
In contrast, permissive parenting, the second style, involves low demands and high responsiveness. Permissive parents are lenient, allowing considerable freedom without consistent discipline. While this approach fosters creativity, it may lead to a lack of self-control in children.
The third style, authoritative parenting, balances high demands with high responsiveness. Authoritative parents set clear expectations while nurturing their children. This approach encourages independence, social competence, and self-esteem, striking a healthy balance between discipline and warmth.
Neglectful or uninvolved parenting, the fourth style, is characterized by low demands and low responsiveness. Neglectful parents are disengaged, showing little interest in their child’s life. This style can lead to emotional and behavioral issues due to the lack of support and guidance.
The fifth style, helicopter parenting, involves excessive hovering and overprotectiveness. Helicopter parents micromanage their child’s life, hindering the development of problem-solving skills and independence. While well-intentioned, this approach can lead to anxiety and low self-confidence in children.
Understanding these parenting styles empowers parents to make informed decisions, tailoring their approach to their child’s unique needs and fostering a nurturing, supportive environment for healthy growth and development.
🌐 Sources
- Verywell Family – Understanding the Four Parenting Styles
- Psychology Today – The Impact of Parenting Styles
This post is for informational purposes only.Invest responsibly.No guarantees of results. Seek professional guidance before investing.Consult experts for personalized advice. Please note that I am not a SEBI registered investment advisor. The information provided in this article is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be construed as financial advice. Always consult with a qualified and SEBI registered financial professional before making any investment decisions.Follows Google policies.Not affiliated with Investopedia.com. investopedia.co.in Independent site.